Importing Models From Keras to Deeplearning4j
Contents
- Getting started
- Project setup
- DL4J and keras models
- Loading model configurations
- Loading model configurations and weights
- Available options
- Troubleshooting
- Model zoo
- Why Keras?
The deeplearning4j-modelimport module provides routines for importing neural network models originally configured
and trained using Keras, a popular Python deep learning library that provides abstraction
layers on top of TensorFlow, Theano and CNTK
backends. You can learn more about saving Keras models on the Keras FAQ Page. Details about the Keras features matched in Deeplearning4j are through the link.
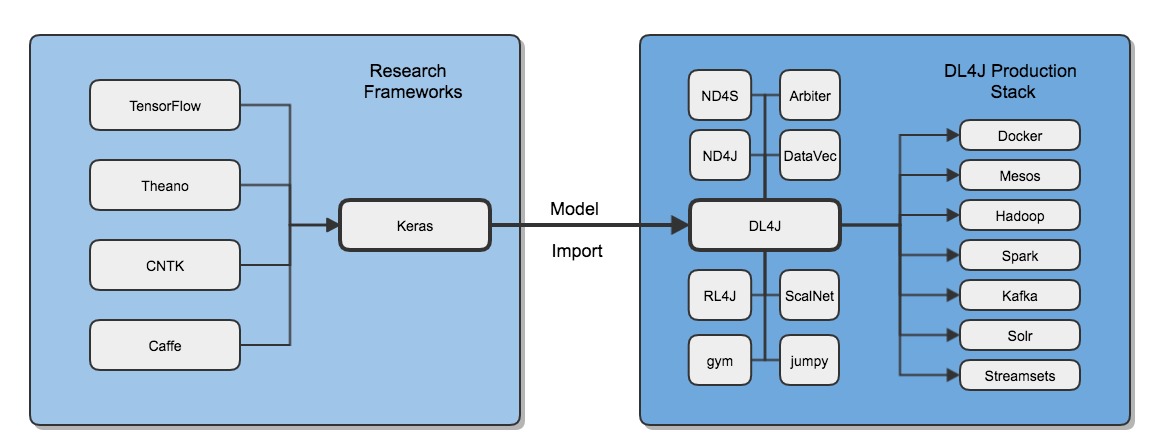
Once you have imported your model into DL4J, our full production stack is at your disposal. Please check here for a complete list of keras features supported through model import.
- This module is targeted at users mainly familiar with writing their models in python with keras.
- It allows users to import their models into the DL4J ecosphere for either further training or evaluation purposes.
- You should use this module when the experimentation phase of your project is completed and you need to ship your models to production.
- Source code for the
modelimportmodule can be found here. - There is often a gap between the production system of a company and the experimental setup of its data scientists. The
modelimportmodule allows data scientists to write their models in python, but still seamlessly integrate with the production stack.
Getting started: Keras Model Import Video
Below is a video tutorial demonstrating working code to load a Keras model into Deeplearning4j and validating the working network. Instructor Tom Hanlon provides an overview of a simple classifier over Iris data built in Keras with a Theano backend, and exported and loaded into Deeplearning4j:
If you have trouble viewing the video, please click here to view it on YouTube.
Project setup & configuring your IDE
Edit your pom.xml adding the following dependency
<dependency>
<groupId>org.deeplearning4j</groupId>
<artifactId>deeplearning4j-modelimport</artifactId>
<version>${dl4j.version}</version>
</dependency>
DL4J and Keras models
Using the Keras Model Import feature you have the following options. Note that Keras has two types of networks, Sequential and functional Model. Keras Sequential model is equivalent to DeepLearning4J’s MultiLayerNetwork. Keras functional Model is equivalent to DeepLearning4J’s ComputationGraph.
To use this, you would save the model in Keras to a JSON file, the DeepLearning4J options available are.
- Sequential Model
- Sequential Model with updater to allow further training
- Functional Model
- Functional Model with updater for further training
Loading only model configurations
To only load the model architecture or configuration, DL4J supports the following two methods.
- Sequential Model Configuration import, saved in Keras with model.to_json()
MultiLayerNetworkConfiguration modelConfig = KerasModelImport.importKerasSequentialConfiguration("PATH TO YOUR JSON FILE)
- ComputationGraph Configuration import, saved in Keras with model.to_json()
ComputationGraphConfiguration computationGraphConfig = KerasModelImport.importKerasModelConfiguration("PATH TO YOUR JSON FILE)
Loading model configuration and saved weights
In this case you would save both the JSON config and the weights from the trained model in Keras. The weights are saved in an H5 formatted file. In Keras you can save the weights and the model configuration into a single H5 file, or you can save the config in a separate file.
- Sequential Model single file
MultiLayerNetwork network = KerasModelImport.importKerasSequentialModelAndWeights("PATH TO YOUR H5 FILE")
The network would be ready to use for inference by passing it input data, formatted, transformed, and normalized in the same manner that the original data was and calling network.output.
- Sequential Model one file for config one file for weights.
MultiLayerNetwork network = KerasModelImport.importKerasSequentialModelAndWeights("PATH TO YOUR JSON FILE","PATH TO YOUR H5 FILE")
Additional Options
The model import feature includes an enforceTrainingConfig parameter.
If you want to import a pre-trained model only for inference, then you should set enforceTrainingConfig=false. Unsupported training-only configurations generate warnings but model import will proceed.
If you want to import a model for training and want to ensure the resulting model matches a trained Keras model as closely as possible, then you should set enforceTrainingConfig=true. In that case, unsupported training-only configurations will throw an UnsupportedKerasConfigurationException and stop model import.
Troubleshooting
An IncompatibleKerasConfigurationException message indicates that you are attempting to import a Keras model configuration
that is not currently supported in Deeplearning4j (either because model import does not cover it, or DL4J does not implement the model, layer, or feature).
Once you have imported your model we recommend our own modelserializer class for further saving and reloading of your model.
You can inquire further by visiting the DL4J gitter channel. You might consider filing a feature request via Github so that this missing functionality can be placed on the DL4J development roadmap or even sending us a pull request with the necessary changes!
Check back for frequent updates to both the model import module and to this page!
Popular Model Support and Model Zoo
VGG16 and other pre-trained models are widely used for demonstration purposes and for retraining for a specific use case. We are proud to announce support for VGG16 import along with some helper functions to properly format and normalize data for ingest, and helper functions to convert the numeric output to labelled text classes.
In addition to being able to import pre-trained Keras models, DeepLearning4j will actively add models to our own model zoo.
Why Keras?
Keras is a layer of abstraction that sits atop Python libraries like Theano, Tensorflow CNTK, providing an easier to use interface for deep learning.
To define a layer in a framework like Theano, you have to precisely define the weights, biases, activation functions and how your input data will be transformed into outputs. Moreover, you need to deal with backpropagation and updating those weights and biases. Keras wraps all that. It gives you prefab layers that encompass those calculations and updates.
With Keras, the only thing you define is the shape of the input, the shape of the output, and how you want to calculate the loss. Keras ensures that all the layers are the right size, and that the error gets backpropagated properly.
More information is also available here.