Quickstart Guide
This is everything you need to run DL4J examples and begin your own projects.
We recommend that you join our Gitter Live Chat. Gitter is where you can request help and give feedback, but please do use this guide before asking questions we’ve answered below. If you are new to deep learning, we’ve included a road map for beginners with links to courses, readings and other resources. If you need an end to end tutorial to get started (including setup), then please go to our getting started.
A Taste of Code
Deeplearning4j is a domain-specific language to configure deep neural networks, which are made of multiple layers. Everything starts with a MultiLayerConfiguration, which organizes those layers and their hyperparameters.
Hyperparameters are variables that determine how a neural network learns. They include how many times to update the weights of the model, how to initialize those weights, which activation function to attach to the nodes, which optimization algorithm to use, and how fast the model should learn. This is what one configuration would look like:
MultiLayerConfiguration conf = new NeuralNetConfiguration.Builder()
.iterations(1)
.weightInit(WeightInit.XAVIER)
.activation("relu")
.optimizationAlgo(OptimizationAlgorithm.STOCHASTIC_GRADIENT_DESCENT)
.learningRate(0.05)
// ... other hyperparameters
.list()
.backprop(true)
.build();
With Deeplearning4j, you add a layer by calling layer on the NeuralNetConfiguration.Builder(), specifying its place in the order of layers (the zero-indexed layer below is the input layer), the number of input and output nodes, nIn and nOut, as well as the type: DenseLayer.
.layer(0, new DenseLayer.Builder().nIn(784).nOut(250)
.build())
Once you’ve configured your net, you train the model with model.fit.
Prerequisites
- Java (developer version) 1.7 or later (Only 64-Bit versions supported)
- Apache Maven (automated build and dependency manager)
- IntelliJ IDEA or Eclipse
- Git
You should have these installed to use this QuickStart guide. DL4J targets professional Java developers who are familiar with production deployments, IDEs and automated build tools. Working with DL4J will be easiest if you already have experience with these.
If you are new to Java or unfamiliar with these tools, read the details below for help with installation and setup. Otherwise, skip to DL4J Examples.
Java
If you don’t have Java 1.7 or later, download the current Java Development Kit (JDK) here. To check if you have a compatible version of Java installed, use the following command:
java -version
Please make sure you have a 64-Bit version of java installed, as you will see an error telling you no jnind4j in java.library.path if you decide to try to use a 32-Bit version instead.
Apache Maven
Maven is a dependency management and automated build tool for Java projects. It works well with IDEs such as IntelliJ and lets you install DL4J project libraries easily. Install or update Maven to the latest release following their instructions for your system. To check if you have the most recent version of Maven installed, enter the following:
mvn --version
If you are working on a Mac, you can simply enter the following into the command line:
brew install maven
Maven is widely used among Java developers and it’s pretty much mandatory for working with DL4J. If you come from a different background, and Maven is new to you, check out Apache’s Maven overview and our introduction to Maven for non-Java programmers, which includes some additional troubleshooting tips. Other build tools such as Ivy and Gradle can also work, but we support Maven best.
IntelliJ IDEA
An Integrated Development Environment (IDE) allows you to work with our API and configure neural networks in a few steps. We strongly recommend using IntelliJ, which communicates with Maven to handle dependencies. The community edition of IntelliJ is free.
There are other popular IDEs such as Eclipse and Netbeans. However, IntelliJ is preferred, and using it will make finding help on Gitter Live Chat easier if you need it.
Git
Install the latest version of Git. If you already have Git, you can update to the latest version using Git itself:
$ git clone git://git.kernel.org/pub/scm/git/git.git
DL4J Examples in a Few Easy Steps
-
Use the command line to enter the following:
$ git clone https://github.com/deeplearning4j/dl4j-examples.git $ cd dl4j-examples/ $ mvn clean install -
Open IntelliJ and choose Import Project. Then select the main ‘dl4j-examples’ directory. (Note: the example in the illustration below refers to an outdated repository named dl4j-0.4-examples. However, the repository that you will download and install will be called dl4j-examples).
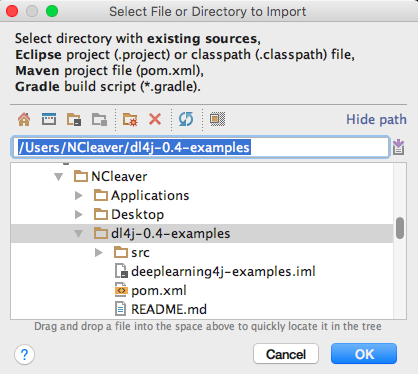
-
Choose ‘Import project from external model’ and ensure that Maven is selected.
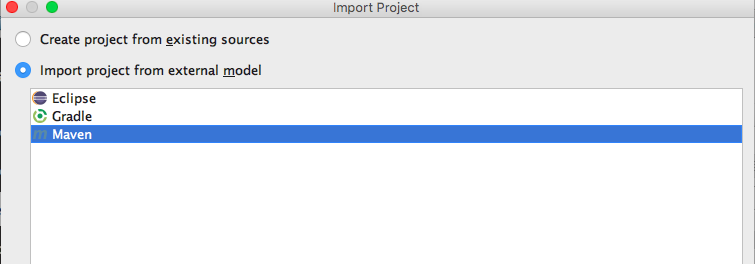
-
Continue through the wizard’s options. Select the SDK that begins with
jdk. (You may need to click on a plus sign to see your options…) Then click Finish. Wait a moment for IntelliJ to download all the dependencies. You’ll see the horizontal bar working on the lower right. -
Pick an example from the file tree on the left.
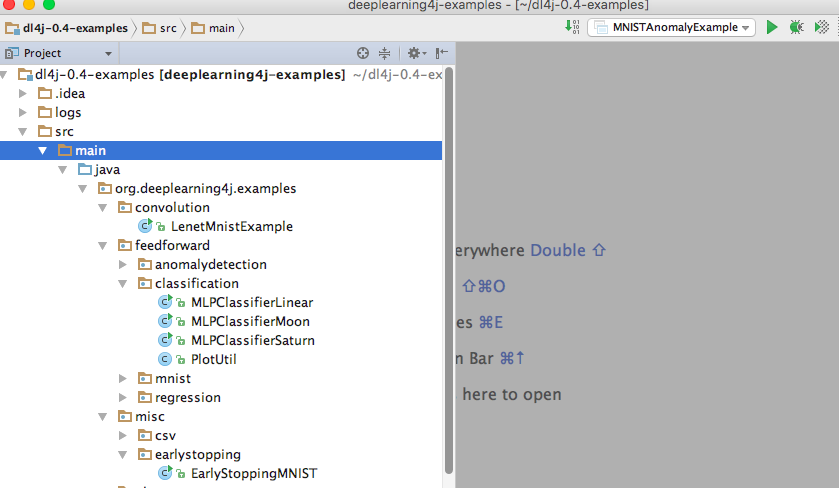 Right-click the file to run.
Right-click the file to run.
Using DL4J In Your Own Projects: Configuring the POM.xml File
To run DL4J in your own projects, we highly recommend using Maven for Java users, or a tool such as SBT for Scala. The basic set of dependencies and their versions are shown below. This includes:
deeplearning4j-core, which contains the neural network implementationsnd4j-native-platform, the CPU version of the ND4J library that powers DL4Jdatavec-api- Datavec is our library vectorizing and loading data
Every Maven project has a POM file. Here is how the POM file should appear when you run your examples.
Within IntelliJ, you will need to choose the first Deeplearning4j example you’re going to run. We suggest MLPClassifierLinear, as you will almost immediately see the network classify two groups of data in our UI. The file on Github can be found here.
To run the example, right click on it and select the green button in the drop-down menu. You will see, in IntelliJ’s bottom window, a series of scores. The rightmost number is the error score for the network’s classifications. If your network is learning, then that number will decrease over time with each batch it processes. At the end, this window will tell you how accurate your neural-network model has become:
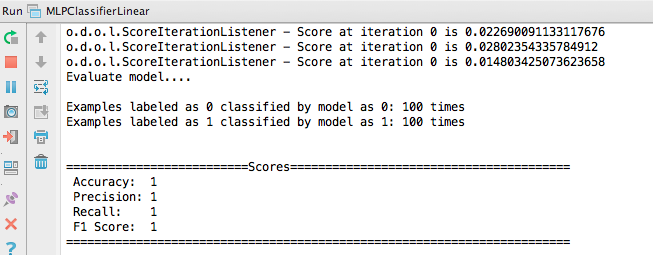
In another window, a graph will appear, showing you how the multilayer perceptron (MLP) has classified the data in the example. It will look like this:
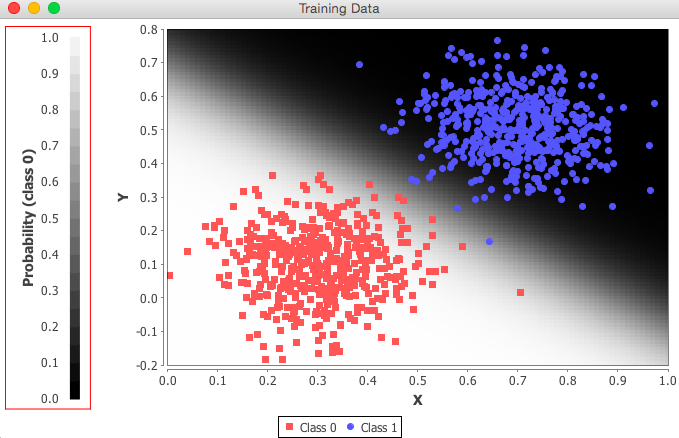
Congratulations! You just trained your first neural network with Deeplearning4j. Now, why don’t you try our next tutorial: MNIST for Beginners, where you’ll learn how to classify images.
Next Steps
- Join us on Gitter. We have three big community channels.
- DL4J Live Chat is the main channel for all things DL4J. Most people hang out here.
- Tuning Help is for people just getting started with neural networks. Beginners please visit us here!
- Early Adopters is for those who are helping us vet and improve the next release. WARNING: This is for more experienced folks.
- Read the introduction to deep neural networks or one of our detailed tutorials.
- Check out the more detailed Comprehensive Setup Guide.
- Browse the DL4J documentation.
- Python folks: If you plan to run benchmarks on Deeplearning4j comparing it to well-known Python framework [x], please read these instructions on how to optimize heap space, garbage collection and ETL on the JVM. By following them, you will see at least a 10x speedup in training time.
Additional links
- Deeplearning4j artifacts on Maven Central
- ND4J artifacts on Maven Central
- Datavec artifacts on Maven Central
- Scala code for UCI notebook
Troubleshooting
Q: I’m using a 64-Bit Java on Windows and still get the no jnind4j in java.library.path error
A: You may have incompatible DLLs on your PATH. To tell DL4J to ignore those, you have to add the following as a VM parameter (Run -> Edit Configurations -> VM Options in IntelliJ):
-Djava.library.path=""
Q: SPARK ISSUES I am running the examples and having issues with the Spark based examples such as distributed training or datavec transform options.
A: You may be missing some dependencies that Spark requires. See this Stack Overflow discussion for a discussion of potential dependency issues. Windows users may need the winutils.exe from Hadoop.
Download winutils.exe from https://github.com/steveloughran/winutils and put it into the null/bin/winutils.exe (or create a hadoop folder and add that to HADOOP_HOME)
Troubleshooting: Debugging UnsatisfiedLinkError on Windows
Windows users might be seeing something like:
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ExceptionInInitializerError
at org.deeplearning4j.nn.conf.NeuralNetConfiguration$Builder.seed(NeuralNetConfiguration.java:624)
at org.deeplearning4j.examples.feedforward.anomalydetection.MNISTAnomalyExample.main(MNISTAnomalyExample.java:46)
Caused by: java.lang.RuntimeException: org.nd4j.linalg.factory.Nd4jBackend$NoAvailableBackendException: Please ensure that you have an nd4j backend on your classpath. Please see: http://nd4j.org/getstarted.html
at org.nd4j.linalg.factory.Nd4j.initContext(Nd4j.java:5556)
at org.nd4j.linalg.factory.Nd4j.(Nd4j.java:189)
... 2 more
Caused by: org.nd4j.linalg.factory.Nd4jBackend$NoAvailableBackendException: Please ensure that you have an nd4j backend on your classpath. Please see: http://nd4j.org/getstarted.html
at org.nd4j.linalg.factory.Nd4jBackend.load(Nd4jBackend.java:259)
at org.nd4j.linalg.factory.Nd4j.initContext(Nd4j.java:5553)
... 3 more
If that is the issue, see this page. In this case replace with “Nd4jCpu”.
Eclipse setup without Maven
We recommend and use Maven and Intellij. If you prefer Eclipse and dislike Maven here is a nice blog post to walk you through an Eclipse configuration.
DL4J Overview
Deeplearning4j is a framework that lets you pick and choose with everything available from the beginning. We’re not Tensorflow (a low-level numerical computing library with automatic differentiation) or Pytorch. For more details, please see our deep learning library compsheet. Deeplearning4j has several subprojects that make it easy-ish to build end-to-end applications.
If you’d like to deploy models to production, you might like our model import from Keras.
Deeplearning4j has several submodules. These range from a visualization UI to distributed training on Spark. For an overview of these modules, please look at the Deeplearning4j examples on Github.
To get started with a simple desktop app, you need two things: An nd4j backend and deeplearning4j-core. For more code, see the simpler examples submodule.
If you want a flexible deep-learning API, there are two ways to go. You can use nd4j standalone See our nd4j examples or the computation graph API.
If you want distributed training on Spark, you can see our Spark page Keep in mind that we cannot setup Spark for you. If you want to set up distributed Spark and GPUs, that is largely up to you. Deeplearning4j simply deploys as a JAR file on an existing Spark cluster.
If you want Spark with GPUs, we recommend Spark with Mesos.
If you want to deploy on mobile, you can see our Android page.
We deploy optimized code for various hardware architectures natively. We use C++ based for loops just like everybody else. For that, please see our C++ framework libnd4j.
Deeplearning4j has two other notable components:
- Arbiter: hyperparameter optimization and model evaluation
- DataVec: built-in ETL for machine-learning data pipelines
Overall, Deeplearning4j is meant to be an end-to-end platform for building real applications. Not just a tensor library with automatic differentiation. If you want that, that’s in ND4J and it’s called samediff. Samediff is still in alpha, but if you want to take a crack at contributing, please come in to our live chat on Gitter.
Lastly, if you are benchmarking Deeplearnin4j, please consider coming in to our live chat and asking for tips. Deeplearning4j has all the knobs but some may not work as the Python frameworks to do. You have to build Deeplearning4j from source for some applications.
Other Deep Learning Tutorials
- Restricted Boltzmann Machines
- Eigenvectors, Covariance, PCA and Entropy
- LSTMs and Recurrent Networks
- Introduction to Deep Neural Networks
- Convolutional Networks
- Deep Learning Notebook-Based Tutorials
- ND4J: A Tensor Library for the JVM
- MNIST for Beginners
- Glossary of Deep-Learning and Neural-Net Terms
- Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)
- Reinforcement Learning for Java and Scala
- Word2vec, Neural Word Embeddings and Node2vec for Java