DL4J Comprehensive Setup Guide
This page builds on the instructions in the Quick Start Guide, and provides additional details and some troubleshooting steps. Seriously, go and read that page first before you proceed with this. It’s the easy way to start with DL4J.
This is a multistep install. We highly recommend you join our Gitter Live Chat if you have questions or feedback, so we can walk you through it. If you’re feeling anti-social or brashly independent, you’re still invited to lurk and learn. In addition, if you are utterly new to deep learning, we’ve got a road map of what to learn when you’re starting out.
After following the steps in the Quick Start Guide, please read the following:
- Detailed Walkthrough
- DL4J Examples In Eclipse
- Troubleshooting
- Reproducible Results
- Scala Version
- CPU/GPU Optimizations
- Next Steps
DL4J Examples: A Detailed Walkthrough
This section provides a more comprehensive version of the steps contained in the quickstart guide.
-
Type the following into your command line to see if you have Git.
git --version - If you do not, install git.
- In addition, set up a Github account and download GitHub for Mac or Windows.
- For Windows, find “Git Bash” in your Startup Menu and open it. The Git Bash terminal should look like cmd.exe.
-
cdinto the directory where you want to place the DL4J examples. You may want to create a new one withmkdir dl4j-examplesand thencdinto that. Then run:git clone https://github.com/deeplearning4j/dl4j-examples - Make sure the files were downloaded by entering
ls. - Now open IntelliJ.
- Click on the “File” menu, and then on “Import Project” or “New Project from Existing Sources”. This will give you a local file menu.
- Select the directory that contains the DL4J examples.
- In the next window, you will be presented with a choice of build tools. Select Maven.
- Check the boxes for “Search for projects recursively” and “Import Maven projects automatically” and click “Next.”
- Make sure your JDK/SDK is set up, and if it’s not, click on the plus sign at the bottom of the SDK window to add it.
- Then click through until you are asked to name the project. The default project name should do, so hit “Finish”.
Using DL4J Examples in Eclipse
In IntelliJ, it is simply sufficient to import the examples as described in the quickstart guide. In order to use the example in Eclipse, an additional step is required.
After running a git clone, run the following command in your command line:
mvn eclipse:eclipse
This will create an Eclipse project that you can then import.
After many years using Eclipse, we recommend IntelliJ, which has a similar interface. Eclipse’s monolithic architecture has a tendency to cause strange errors in our code and others’.
If you use Eclipse, you will need to install the Maven plugin for Eclipse: eclipse.org/m2e/.
Michael Depies has written this guide to installing Deeplearning4j on Eclipse.
Using DL4J Examples in Eclipse with direct checkout from GIT via the Maven plugin
If you just want to get the examples running within Eclipse and without using command line at all you can also directly checkout the project from Eclipse’s built-in Source Control Management (SCM):
- In an empty workspace, import via “Check out Maven Project from SCM” and click on “Next”
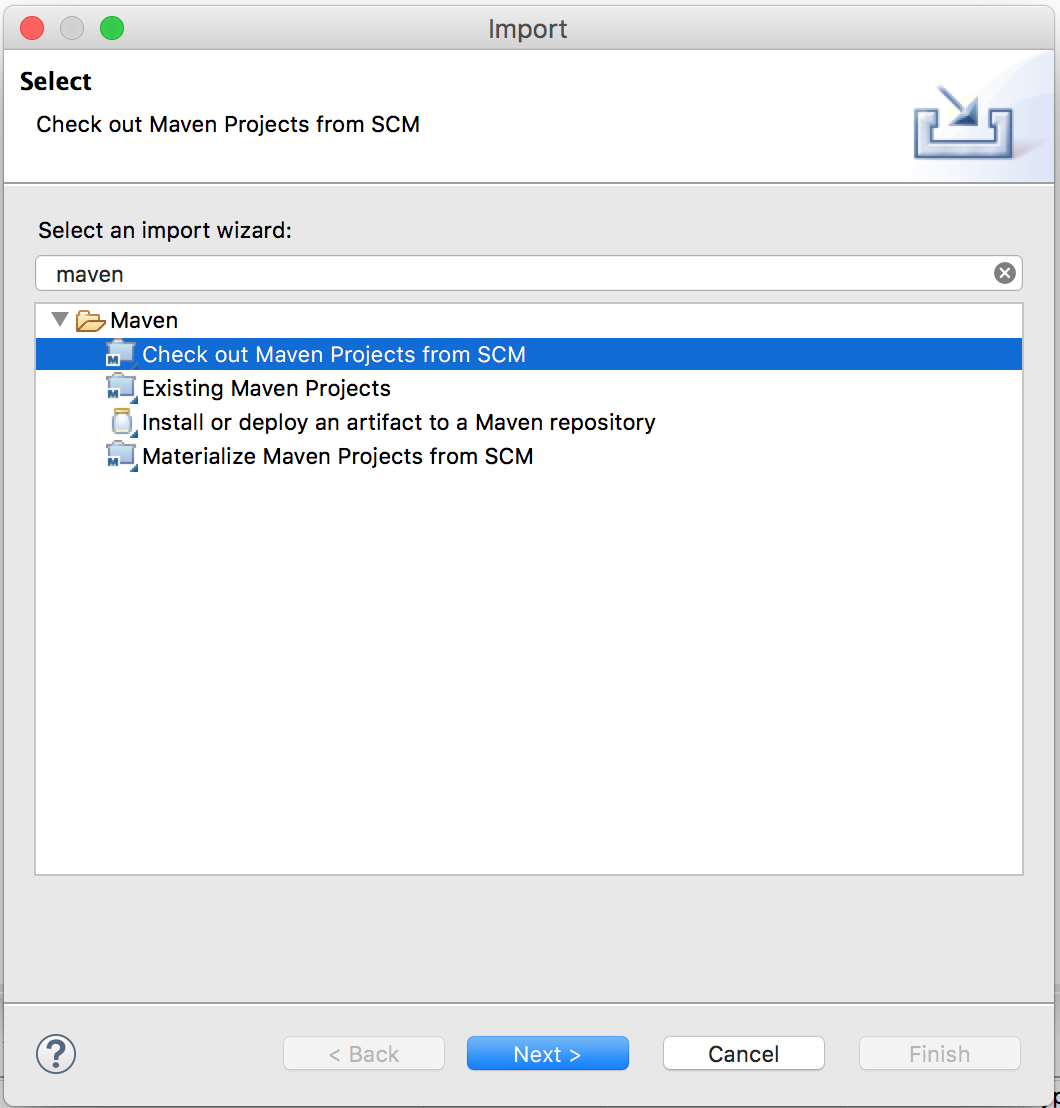
- Paste the git repo url: https://github.com/deeplearning4j/dl4j-examples.git (In case you don’t see “git” in the dropdown click on the “Find more SCM connectors in the m2e Marketplace” link on the bottom, right of the dialog
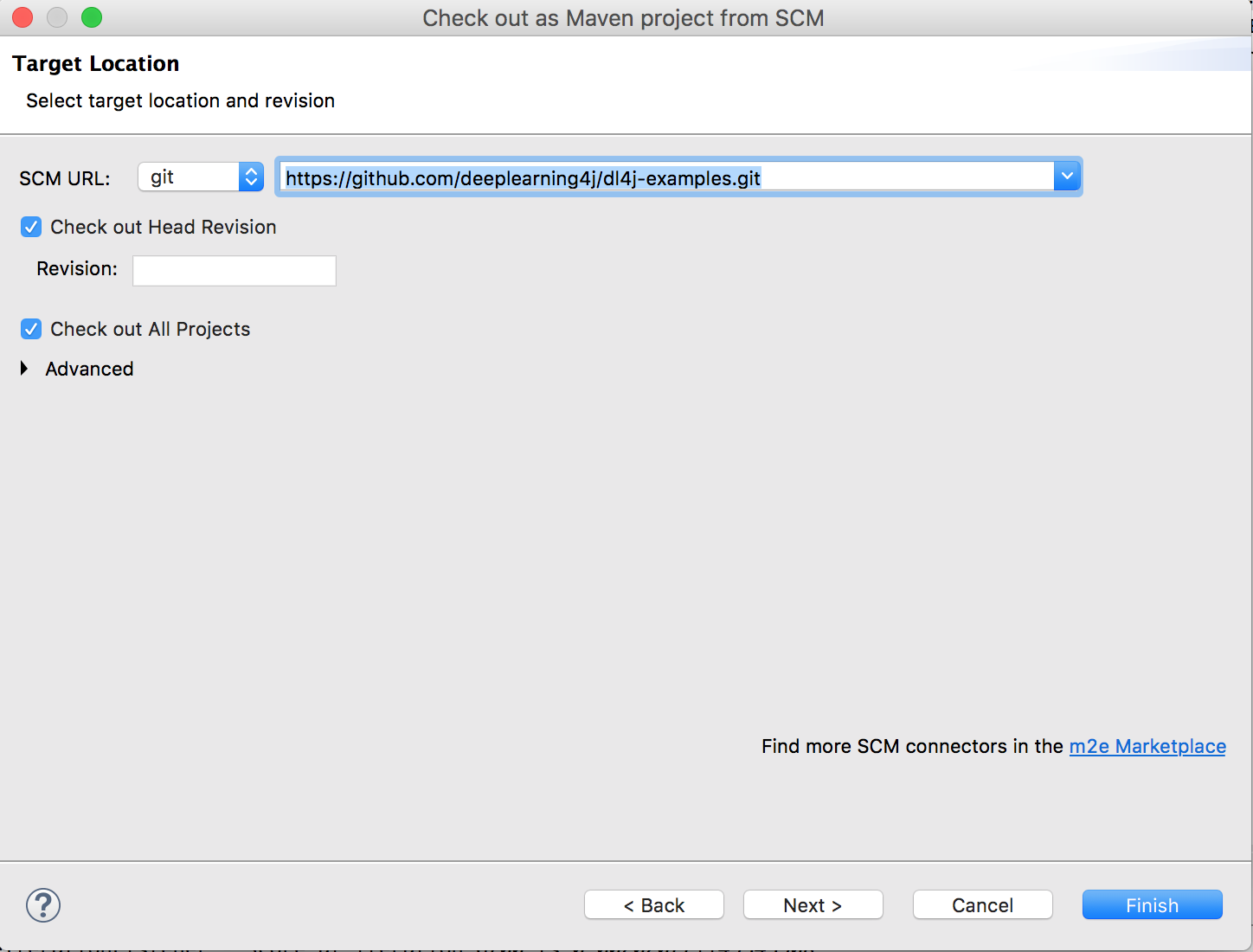
- Click on Finish (..and wait, it will take some time)
You might get some errors in the pom.xml validator, ignore those for now.
Test it!
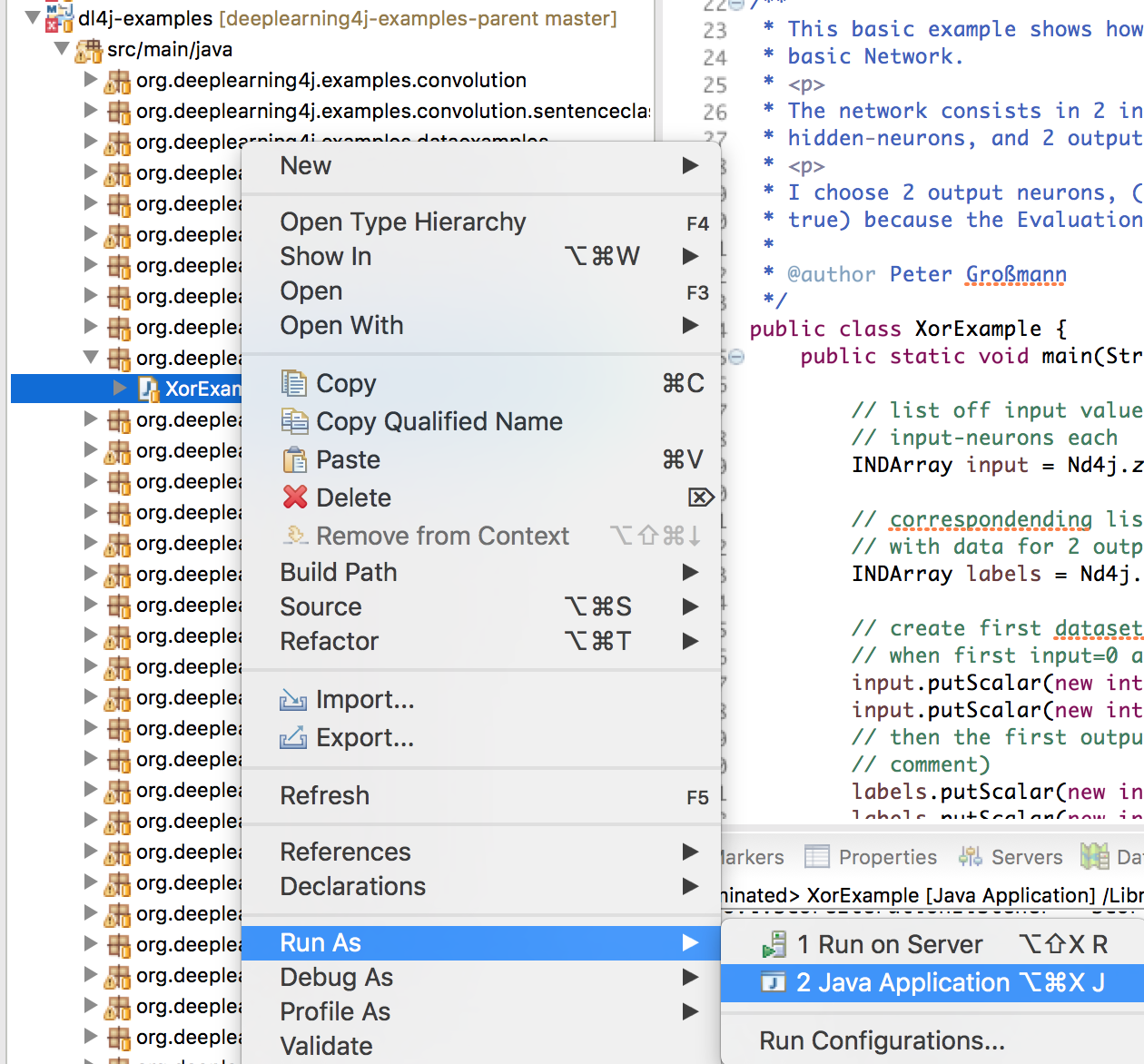
Find the file called XorExample.java in the org.deeplearning4j.examples.feedforward.xor packege in the src/main/java folder of the dl4j-examples project. Right-click and “Run as Java-Application”:
You should see an output like this:
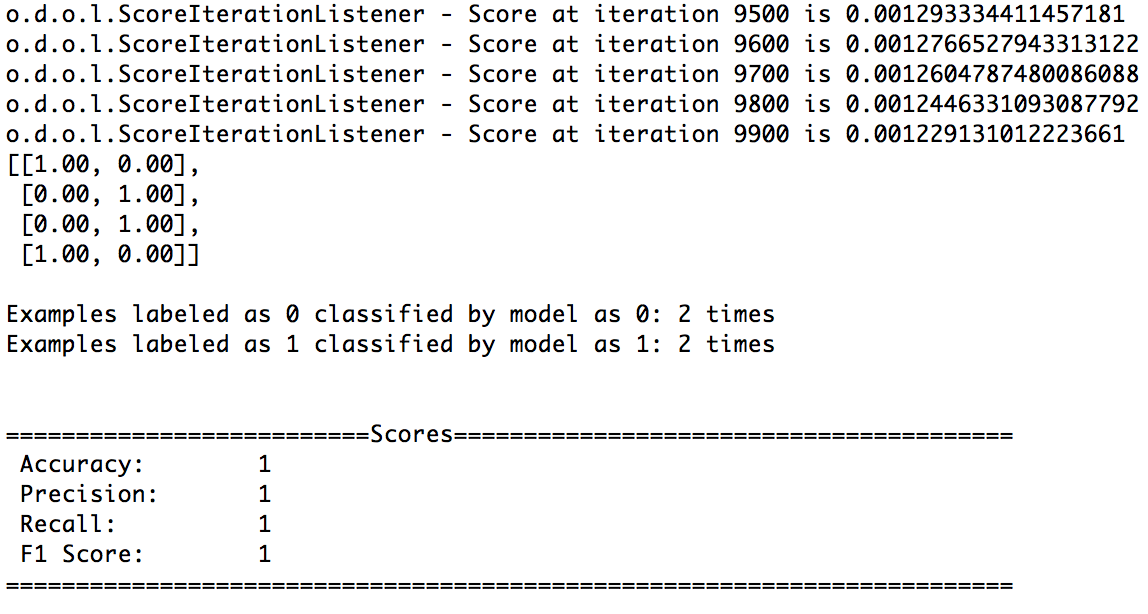
Congratulations, you can start coding!
Model Zoo
As of 0.9.0 (or 0.8.1-SNAPSHOT), Deeplearning4j has a new native model zoo that can be accessed and instantiated directly from DL4J. Gone are the days of copying model configs from Github. The model zoo also includes pretrained weights for different datasets that are downloaded automatically and checked for integrity. 🚀
Setting up a pretrained model with weights trained on ImageNet are as easy as:
ZooModel zooModel = new VGG16();
ComputationGraph pretrainedNet = zooModel.initPretrained(PretrainedType.IMAGENET);
Learn more about the new zoo here.
Troubleshooting
-
Please feel free to ask us about error messages on our Gitter Live Chat. When you post your question, please have the following information ready (it will really speed things up!):
* Operating System (Windows, OSX, Linux) and version * Java version (7, 8) : type java -version in your terminal/CMD * Maven version : type mvn --version in your terminal/CMD * Stacktrace: Please past the error code on Gist and share the link with us: https://gist.github.com/ -
If you have installed DL4J before and now see the examples throwing errors, please update your libraries. With Maven, just update the versions in your POM.xml file to match the latest versions on Maven Central. With source, you can run a
git cloneon ND4J, datavec and DL4J and amvn clean install -DskipTests=true -Dmaven.javadoc.skip=truewithin all three directories, in that order.
note When building or rebuilding from source please see Building Locally for complete instructions.
- When you run an example, you may get a low f1 score, which is the probability that the net’s classification is accurate. In this case, a low f1 doesn’t indicate poor performance, because the examples train on small data sets. We gave them small data sets so they would run quickly. Because small data sets are less representative than large ones, the results they produce will vary a great deal. For example, on the minuscule example data, our deep-belief net’s f1 score currently varies between 0.32 and 1.0.
- Deeplearning4j includes an autocomplete function. If you are unsure which commands are available, press any letter and a drop-down list like this will appear:
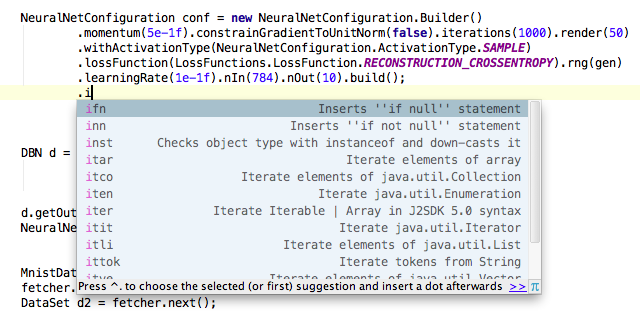
- Here’s the Javadoc for all Deeplearning4j’s classes and methods.
- As the code base grows, installing from source requires more memory. If you encounter a
Permgen errorduring the DL4J build, you may need to add more heap space. To do that, you’ll need to find and alter your hidden.bash_profilefile, which adds environmental variables to bash. To see those variables, enterenvin the command line. To add more heap space, enter this command in your console: echo “export MAVEN_OPTS=”-Xmx512m -XX:MaxPermSize=512m”” > ~/.bash_profile - Older versions of Maven, such as 3.0.4, are likely to throw exceptions like a NoSuchMethodError. This can be fixed by upgrading to the latest version of Maven, which is currently 3.3.x. To check your Maven version, enter
mvn -vin the command line. - After you install Maven, you may receive a message like this:
mvn is not recognised as an internal or external command, operable program or batch file.That means you need Maven in your PATH variable, which you can change like any other environmental variable. - If you see the error
Invalid JDK version in profile 'java8-and-higher': Unbounded range: [1.8, for project com.github.jai-imageio:jai-imageio-core com.github.jai-imageio:jai-imageio-core:jar:1.3.0, you may have a Maven issue. Please update to version 3.3.x. - To compile some ND4J dependencies, you need to install some dev tools for C and C++. Please see our ND4J guide.
- The include path for Java CPP doesn’t always work on Windows. One workaround is to take the header files from the include directory of Visual Studio, and put them in the include directory of the Java Run-Time Environment (JRE), where Java is installed. This will affect files such as standardio.h. More information is available here.
- Instructions on monitoring your GPUs are here.
- One major reason to use Java is its pre-baked diagnostics in the JVisualVM. If you have Java installed, just enter
jvisualvmin your command line and you’ll get visuals on your CPU, Heap, PermGen, Classes and Threads. One useful view: Click on theSamplertab on the upper right, and then select the CPU or Memory button for visuals.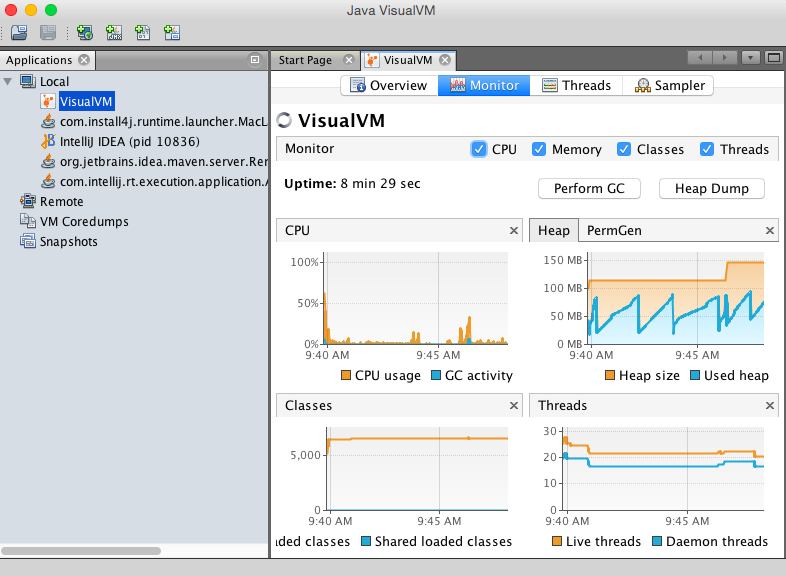
- Some problems encountered using DL4J may be due to a lack of familiarity with the ideas and techniques of machine learning. We strongly encourage all Deeplearning4j users to rely on resources beyond this website to understand the fundamentals. We’ve included a list of educational resources for machine and deep learning on this page. While we’ve partially documented DL4J, parts of the code essentially remain a raw, domain-specific language for deep learning.
- When using
deeplearning4j-nlpfrom a Clojure application and building an uberjar with Leiningen, it is necessary to specify the following in theproject.cljso that the akkareference.confresource files are properly merged.:uberjar-merge-with {#"\.properties$" [slurp str spit] "reference.conf" [slurp str spit]}. Note that the first entry in the map for .properties files is the usual default). If this is not done, the following exception will be thrown when trying to run from the resulting uberjar:Exception in thread "main" com.typesafe.config.ConfigException$Missing: No configuration setting found for key 'akka.version'. - Float support is buggy on OSX. If you see NANs where you expect numbers running our examples, switch the data type to
double. - There is a bug in fork-join in Java 7. Updating to Java 8 fixes it. If you get an OutofMemory error that looks like this, fork join is the problem:
java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException: java.lang.OutOfMemoryError….java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinTask.getThrowableException(ForkJoinTask.java:536)
Managed Environments
If you are working in a managed environment like Databricks, Domino or Sense.io, you’ll need to take an additional step. After you’ve followed the local setup above, just run
mvn clean package
in the command line from within the examples directory. Then you can upload the JAR file to the managed environment you’ve chosen.
Reproducible Results
Neural net weights are initialized randomly, which means the model begins learning from a different position in the weight space each time, which may lead it to different local optima. Users seeking reproducible results will need to use the same random weights, which they must initialize before the model is created. They can reinitialize with the same random weight using the following method:
long seed = 6;
MultiLayerConfiguration conf = new NeuralNetConfiguration.Builder()
.seed(seed)
Scala
Our Scala version is here This is a port of keras to scala (a work in progress).
Advanced: Using the Command Line on AWS
If you install Deeplearning4j on an AWS server with a Linux OS, you may want to use the command line to run your first examples, rather than relying on an IDE. In that case, run the git clones and mvn clean installs according to the instruction above. With the installs completed, you can run an actual example with one line of code in the command line. The line will vary depending on the repo version and the specific example you choose.
Here is a template:
java -cp target/nameofjar.jar fully.qualified.class.name
And here is a concrete example, to show you roughly what your command should look like:
java -cp target/dl4j-examples.jar org.deeplearning4j.MLPBackpropIrisExample
That is, there are two wild cards that will change as we update and you go through the examples:
java -cp target/*.jar org.deeplearning4j.*
To make changes to the examples from the command line and run that changed file, you could, for example, tweak MLPBackpropIrisExample in src/main/java/org/deeplearning4j/multilayer and then maven-build the examples again.
###Native CPU and GPU Optimizations
To make best use of your hardware see this page for CPU optimizations.
Native CPU Optimization for DeepLearning4J and ND4J
To make best use of your GPU’s, see this page to configure our data processing Library ND4J for GPU’s.
Next Steps: IRIS Example & Building NNs
In order to get started building neural nets, checkout the Neural Nets Overview for more information.
Take a look at the MNIST tutorial to get running quickly, and check out our guide for restricted Boltzmann machines to understand the basic mechanics of deep-belief networks.
Follow the ND4J Getting Started instructions to start a new project and include necessary POM dependencies.
More Machine Learning Tutorials
For people just getting started with deep learning, the following tutorials and videos provide an easy entrance to the fundamental ideas of deep neural networks:
- Deep Reinforcement Learning
- Deep Convolutional Networks
- Recurrent Networks and LSTMs
- Multilayer Perceptron (MLPs) for Classification
- Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)
- Symbolic Reasoning & Deep Learning
- Using Graph Data with Deep Learning
- AI vs. Machine Learning vs. Deep Learning
- Markov Chain Monte Carlo & Machine Learning
- MNIST for Beginners
- Restricted Boltzmann Machines
- Eigenvectors, PCA, Covariance and Entropy
- Glossary of Deep-Learning and Neural-Net Terms
- Word2vec and Natural-Language Processing
- Deeplearning4j Examples via Quickstart
- Neural Networks Demystified (A seven-video series)
- Inference: Machine Learning Model Server