A Beginner’s Guide to Radial Basis Function Networks
A radial basis function (RBF) is a function that assigns a real value to each input from its domain (it is a real-value function), and the value produced by the RBF is always an absolute value; i.e. it is a measure of distance and cannot be negative.
f(x) = f(||x||)
Euclidean distance, the straight-line distance between two points in Euclidean space, is typically used.
Radial Basis Function Networks
Radial basis functions are used to approximate functions, much as neural networks act as function approximators. The following sum:
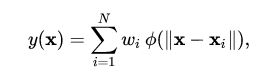
represents a radial basis function network. The radial basis functions act as activation functions.
The approximant f(x) is differentiable with respect to the weights W, which are learned using iterative updater methods commong among neural networks.
Other Machine Learning Tutorials
- Introduction to Neural Networks
- Deep Reinforcement Learning
- Symbolic AI and Deep Learning
- Using Graph Data with Deep Learning
- Recurrent Networks and LSTMs
- Word2Vec: Neural Embeddings for NLP
- Restricted Boltzmann Machines
- Eigenvectors, Covariance, PCA and Entropy
- Neural Networks & Regression
- Convolutional Networks (CNNs)
- Open Datasets for Deep Learning
- Inference: Machine Learning Model Server